What We Do
Minimizing impact, maximizing care with advanced radiation therapy
One of the most important first steps after an unexpected medical diagnosis is gaining a clear understanding of the best way to confidently move forward. At Austin CyberKnife, we are here to help you not only understand which options are available but also match those options to your personal needs.
Whether you’re seeking an alternative to surgery, worried about how radiation affects healthy tissue, or want to learn how the CyberKnife® can minimize the impact on your daily life, we are committed to helping you find a treatment plan that’s right for you.
With access to state-of-the-art technology and dedicated professionals experienced in advanced radiation therapy, we deliver compassionate and quality care for a stress-free experience. If you’d like to discuss your situation with the Austin CyberKnife team, we encourage you to get in touch.
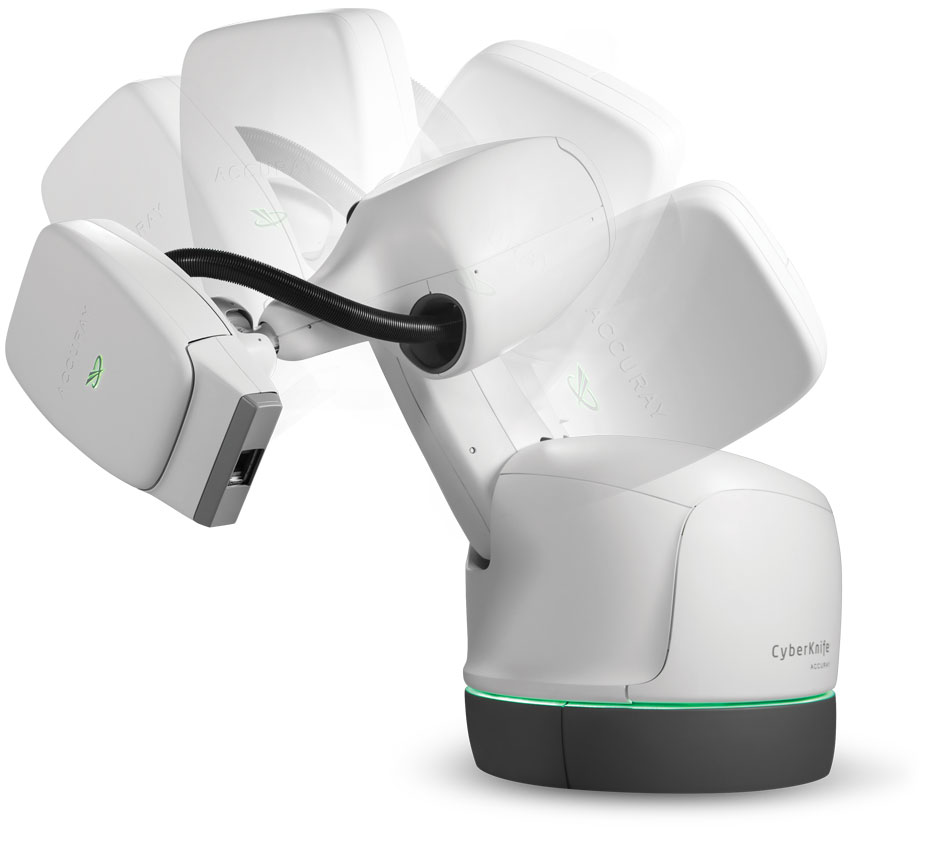
Our Technology
CyberKnife precision delivers a number of unique benefits to patients
Proven Therapy
FDA-approved to treat any part of the body
Safer Treatment
No incisions, anesthesia or hospitalization
Shorter program
1 to 5 visits lasting less than one hour each
Precision Targeted
Surrounding healthy tissues exposed to less radiation


 Douglas Rivera, MD
Douglas Rivera, MD Kirsten A. Warhoe, MD
Kirsten A. Warhoe, MD Paiman Ghafoori, MD
Paiman Ghafoori, MD Shannon D. Cox, MD
Shannon D. Cox, MD Stephen L. Brown, MD
Stephen L. Brown, MD

